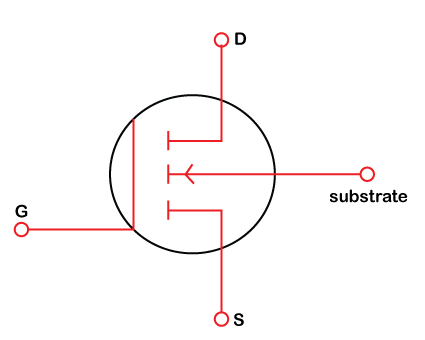
N Channel Depletion Mosfet
For an N-channel enhancement MOSFET V GS(th) is above 0 V. Therefore, even at V GS of 0 V, a depletion MOSFET can conduct current. To turn off a depletion MOSFET the V GS should be lower than the (negative) V GS(th). This is clearly shown in schematic symbols for both. Figure 3 below shows the schematic symbols for. MOSFET can be classified into Enhancement type MOSFET and Depletion type MOSFET. Each of these types are further divided into N-channel MOSFET and P-channel MOSFET. The symbols for each of these types of MOSFETs are shown in the image below.
Webmaster Homepage and contact information.
Download 3com etherlink 10/100 pci nic (3c905-tx) driver. Hobby Electronics Homepage.
Update Dec. 2019. Many micro-controllers today are using 3.3-volt Vcc. This is also true of Raspberry Pi. Download sercomm usb devices driver. I found two MOSFETs that work at 3.3-volts.
The IRFZ44N is an N-channel device rated at 55V and RDS(on) resistance of 0.032 Ohms max. The other is a P-channel device rated at 55V and a RDS(on) of 0.02 Ohms max.
See the following spec sheets:
Also see Test Power MOSFET Transistors, Results, Observations
Here we will learn how power n-channel power MOSFETs operate. In this example I'm using enhancement mode devices. To use depletion mode MOSFETS simply reverse the circuits where an N-channel depletion mode MOSFET will use a variation of the P-channel enhancement mode circuit.
N Channel Depletion Mosfet Rate
In plate 1 we have the symbols for depletion mode and enhancement mode MOSFETs - notice the dashed versus solid lines. In a depletion mode MOSFET gate voltage closes off the conductive channel from source (S) to drain (D). With an enhancement mode MOSFETs gate voltage opens the conductive channel from source to drain.
In the above examples we are switching a LED on/off using power MOSFETs. In the case of the N-channel such as the IRF630 when the gate (G) is greater than 5-volts the LED cuts on. The resistor on the gate of the N-channel MOSFET is used to bleed-off the electric charge from the gate and turn off the MOSFET. The resistor can be 5K-10K.
Plate 4
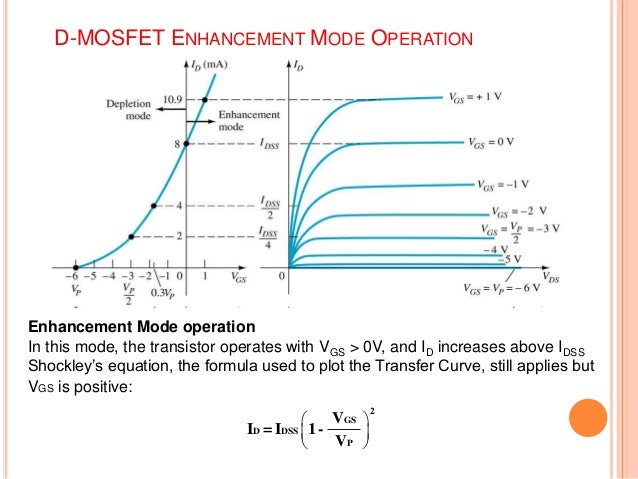
The voltage difference between the gate and source will turn on the MOSFET, but must not exceed a value in the spec sheet known as Vgs. To do so will damage the device. In the case of IRF630 and IRF9630 MOSFETs that value is 20-volts.
Note the internal parasitic suppression diodes are for use with magnetic loads. Not all power MOSFETs have those so check the specifications sheets. These particular transistors are optimized for switching and not for use in audio amplifiers.
Whizz paint brush. The largest use of these circuits is H-bridge motor controls. They are used in conjunction with N-channel MOSFET switches.

Note that Rg (or Rgs) is used to bleed the charges off the MOSFET gates or else they may not turn off.
- Related:
- Why Your MOSFET Transistors Get Hot YouTube
- Issues on Connecting MOSFETs in Parallel YouTube
- Simple Circuits for Testing MOSFET Transistors YouTube
N Channel Depletion Mosfet Program
- New Nov. 2014
- Using the ULN2003A Transistor Array with Arduino YouTube
- Using the TIP120 & TIP120 Darlington Transistors with Arduino YouTube
- Using Power MOSFETS with Arduino YouTube
- Using PNP Bipolar Transistors with Arduino, PIC YouTube
- Using NPN Biploar Transistors with Arduino, PIC YouTube
- How to build a Transistor H-Bridge for Arduino, PIC YouTube
- Build a Power MOSFET H-Bridge for Arduino, PIC YouTube
